Imagine your PLC panel shutting down in the middle of production—just because the UPS failed for two seconds. One tiny power break can stop an entire chemical or pharma line.
That’s exactly why industries use ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) with UPS.
In any manufacturing plant, continuous power is not a luxury—it is a lifeline. PLCs, HMIs, analyzers, and instrumentation circuits must run without interruption.
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) ensures your plant never stops by automatically shifting the load between UPS power and direct mains supply, depending on which source is healthy.
This guide explains ATS for beginners in the simplest possible way, with real examples and calculations.
In this guide, you will learn:
- What an ATS is
- Why ATS is required when we already have a UPS
- How ATS works (simple explanation)
- A real-life example with load calculations
- ATS wiring logic
- Selection criteria + sizing
- Advantages in industrial plants
Let’s start with the basics.
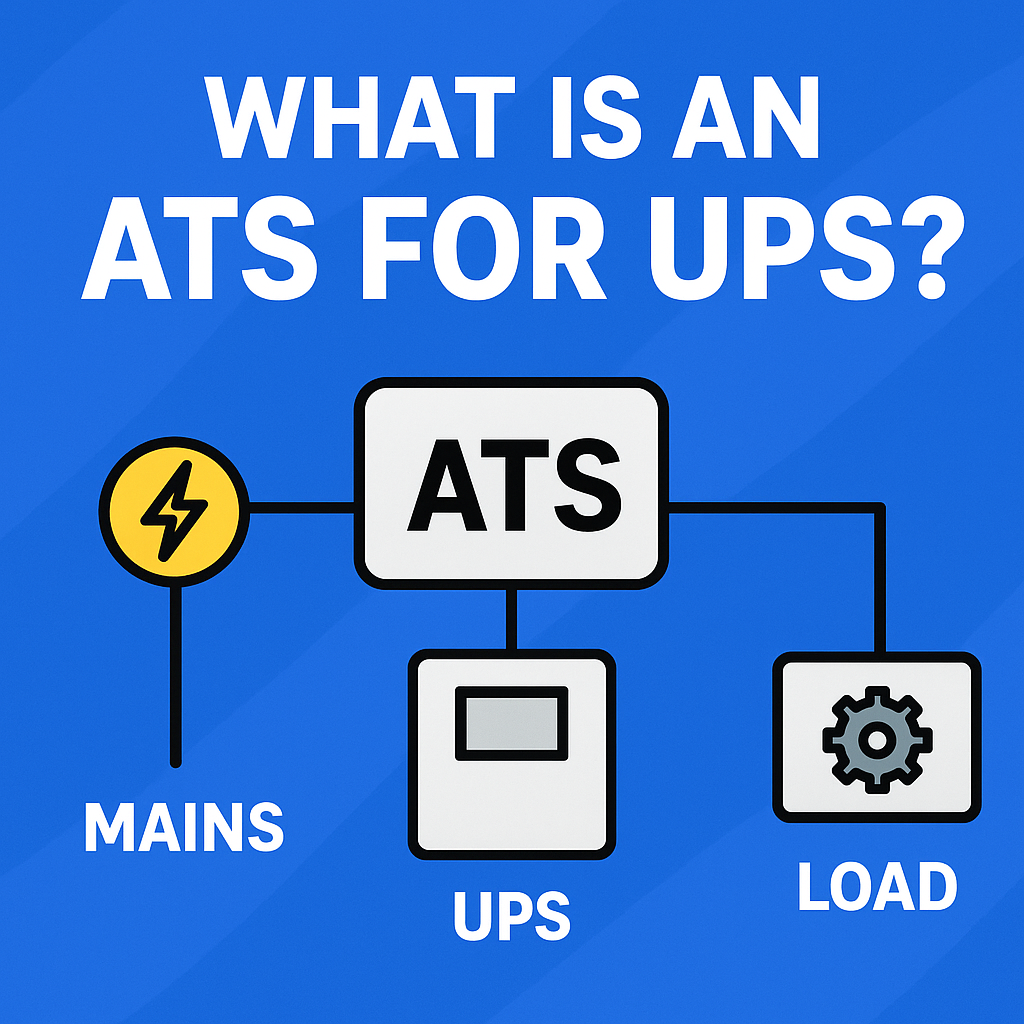
What is an ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) for UPS?
An Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is an intelligent switching device that automatically transfers the load between:
- Primary Power Source → e.g., Mains
- Backup Power Source → e.g., UPS / Generator
When the main source fails, the ATS shifts the load to UPS instantly without requiring a human operator.
In simple words:
ATS = Automatic Power Selector
It chooses the best available power source without interruption.
Why Do We Need an ATS Along With a UPS?
A UPS gives backup power, but it also needs a clean input source.
When mains fail, UPS runs on battery — but when mains return, UPS must shift back safely.
ATS ensures:
- No double supply conflict
- Safe switching between mains and UPS
- Zero downtime for critical equipment
- Protection from voltage fluctuations
- Smooth load transfer
Real-Life Industry Example (Beginner-Friendly)
Let’s assume you have a Control Panel in a chemical plant.
Load connected to UPS:
- PLC System = 0.7 kW
- SCADA Desktop = 0.3 kW
- HMI + Router = 0.2 kW
- Control power for relays = 0.3 kW
➡ Total Load = 1.5 kW (approx)
We want this load to run even if the mains fail.
So we install a 2 kW UPS and an ATS.
Step-by-Step Calculations
1. Load Current Calculation
UPS output voltage = 230 V
Power factor (PF) = 0.85
Total load = 1.5 kW
Current (I) = P / (V × PF)
I = 1500 / (230 × 0.85)
I = 7.68 A
➡ Recommended UPS output breaker = 16 A
➡ Recommended ATS rating = 25 A
2. UPS Sizing Calculation
Rule: UPS should be 1.3 × Load
UPS size = 1.5 kW × 1.3 = 2 kW UPS
This ensures:
- Longer life
- Less heating
- Stable switching
3. Battery Backup Calculation
UPS battery = 24 V
Load = 1.5 kW
UPS efficiency = 0.9
Backup needed = 30 minutes
Battery current = Load / (Voltage × Efficiency)
I = 1500 / (24 × 0.9)
I = 69.4 A
Amp-hour (Ah) = I × Time
Time = 0.5 hr
Ah = 69.4 × 0.5 = 34.7 Ah
➡ Select standard 42 Ah battery (two units)
➡ Better option: 65 Ah for long backup
🔄 How ATS Works – Simple Explanation
Normal Condition (Mains Healthy):
- ATS connects Mains → UPS Input → UPS Output → Load
- UPS charges battery at the same time
If Mains Fails:
- ATS detects voltage drop
- ATS disconnects mains
- UPS instantly supplies power from battery
- Load remains uninterrupted
When Mains Return:
- ATS waits 5–10 seconds (stabilization)
- Switches back to mains
- UPS starts charging again
ATS Wiring Overview (Beginner Diagram)
ATS ensures only one source at a time is connected to the load.
How to Select the Right ATS for UPS
✔ Load in Amps (add 125% safety)
✔ UPS rating
✔ Switching type
- Contactor-based ATS (economical)
- Static Transfer Switch (ultra-fast)
✔ Features you need
- Voltage sensing
- Time delay relay
- Automatic return
- LED status indication
✔ Make/Brand recommended
- Socomec
- Riello
- Schneider
- Eaton
- L&T
Advantages of ATS in Industrial Plants
| Feature | Benefit |
| Automatic switching | Zero downtime |
| Voltage protection | Protects PLC & instruments |
| Safe changeover | No backfeed issues |
| Battery protection | Prevents deep discharge |
| Improves reliability | Reduces plant breakdowns |
Conclusion
An ATS for UPS is one of the most reliable ways to ensure continuous power in chemical and pharma plants. It automatically switches between mains and UPS, protects equipment, prevents downtime, and improves plant reliability.
Whether you are a beginner or a professional, understanding the basics of ATS helps you design safer and more efficient electrical systems.
FAQs
Q1: What does an ATS do in a UPS system?
It automatically switches load from UPS to mains and back based on source health.
Q2: Is ATS required for all PLC panels?
If continuity is critical, yes. ATS prevents shutdowns.
Q3: Will ATS switching cause interruption?
Static ATS = almost zero interruption
Contactor ATS = a few milliseconds
Q4: Can I connect motors through this ATS?
No. This ATS is for control loads, not heavy motors.
Q5: How long will 40 Ah batteries last?
For 1,250 W load → approx. 15–18 minutes.